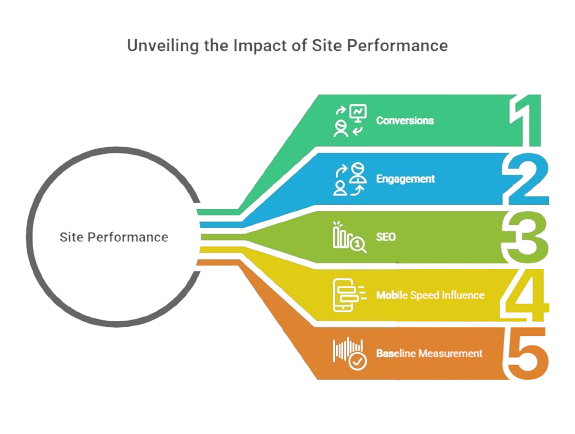
Why performance matters (and how to improve results)
A fast site improves conversions, engagement, and SEO. Because Google uses real-user data (Core Web Vitals), your mobile speed strongly influences rankings. Before optimizing, capture a baseline so you can clearly show the impact later.
Measure now (5 minutes):
- PageSpeed Insights (mobile first): Note LCP, CLS, INP, and the overall score.
- GTmetrix (Waterfall): Record TTFB, total requests, and total page size.
- Pages to test: Homepage, a top blog/product page, and checkout (if WooCommerce).
Create a simple sheet: Page → LCP/CLS/INP → TTFB → Page size → Notes. After each tweak, retest and log the gains.
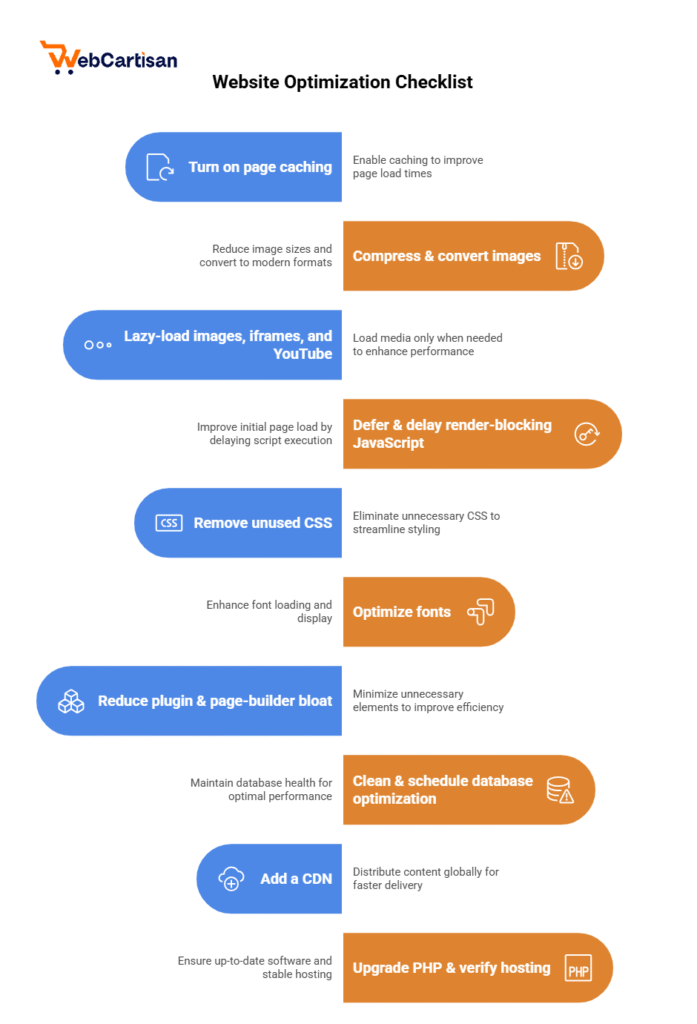
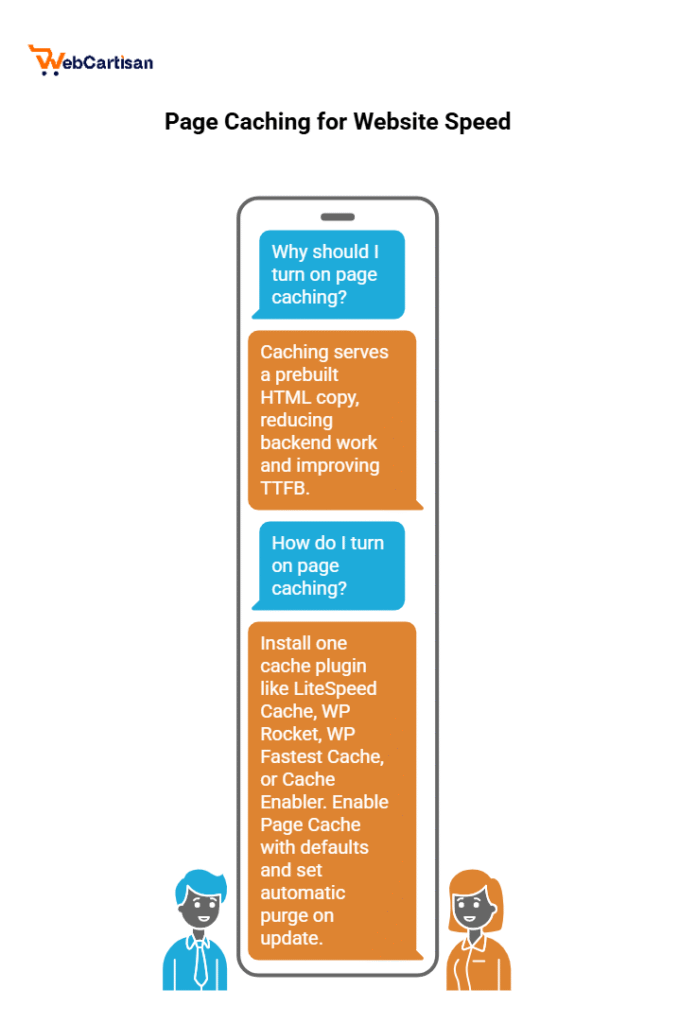
1) Turn on page caching
Why: Caching serves a prebuilt HTML copy instead of rebuilding pages on every visit. Therefore, backend work drops and TTFB improves.
How (no code):
- Install one cache plugin (avoid stacking): LiteSpeed Cache (ideal with LiteSpeed/QUIC hosting), WP Rocket (paid), or WP Fastest Cache/Cache Enabler (free).
- Enable Page Cache with defaults.
Set automatic purge on update so visitors see fresh content after you publish.
WooCommerce: Cart, checkout, and account pages shouldn’t be served from full page cache. Good plugins exclude these automatically.
2) Compress & convert images to WebP/AVIF
Why: Images often make up 50–80% of a page’s weight. As a result, optimizing them slashes load time and improves LCP.
How (5–10 minutes):
- Install ShortPixel, Imagify, or Smush.
- Enable Lossy/Smart compression (or “Aggressive”), Auto WebP (AVIF if available), and Resize large images (max width 1600–1920px).
- Run bulk optimization.
Pro tip: Preload your hero image (many speed plugins offer this) so LCP paints sooner.
3) Lazy-load images, iframes, and YouTube
Why: Lazy loading fetches media only when it’s about to appear on screen. Consequently, the initial render is lighter and faster.
How:
- In LiteSpeed Cache → Page Optimization (or Jetpack Boost/WP Rocket), enable Lazy Load for images and iframes.
- Replace YouTube iframes with a click-to-play thumbnail.

Tip: Exclude the LCP (hero) image from lazy load so it appears immediately.
4) Defer & delay render-blocking JavaScript
Why: When JavaScript blocks rendering, your content waits. If you delay non-critical scripts until interaction, FCP/LCP improves.
How (no code):
- In your speed plugin, toggle Defer JavaScript and Delay JavaScript (load on interaction).
- Test pages. If a menu or slider breaks, add that script to the exclude list.

Order: First enable Defer, then Delay. As a result, you’ll keep interactivity while rendering faster.
5) Remove unused CSS (or build Critical CSS)
Why: Themes and builders ship lots of CSS you don’t need on every page. Trimming it means the browser parses less, so first paint happens sooner.
How:
- Turn on Remove Unused CSS in LiteSpeed/WP Rocket or enable Critical CSS in Jetpack Boost.
- Let the plugin build once; then clear cache.
If you see a brief “unstyled” flash: Rebuild Critical CSS or exclude specific CSS from removal.
6) Optimize fonts (or use a system font stack)
Problem: Remote Google Fonts can delay text paint and cause layout shifts.
Fast fixes:
- Best speed: Switch to a system font stack in your theme (no downloads at all).
- Otherwise, host Google Fonts locally and preload the main weight/styles (via OMGF or your speed plugin).
Outcome: Text paints earlier, CLS drops, and the first impression feels instant.
7) Reduce plugin & page-builder bloat
Why: Each plugin can add CSS/JS everywhere—even where it’s not needed. Because of this, pages bloat over time.
Simple workflow:
- Audit plugins quarterly. Deactivate and remove what you don’t truly need.
- Use Perfmatters or Asset CleanUp to disable plugin assets per page (e.g., load contact form JS only on the Contact page).
- In page builders, prefer fewer sliders, fewer animations, and simpler sections on high-traffic pages.
8) Clean & schedule database optimization
Why: Trimming post revisions, transients, and spam speeds queries and keeps backups smaller.
How (3 minutes):
- Install WP-Optimize (or use your cache plugin’s DB tab).
- Schedule weekly cleanups during off-peak hours.
- Keep 2–3 post revisions per post if you edit often.
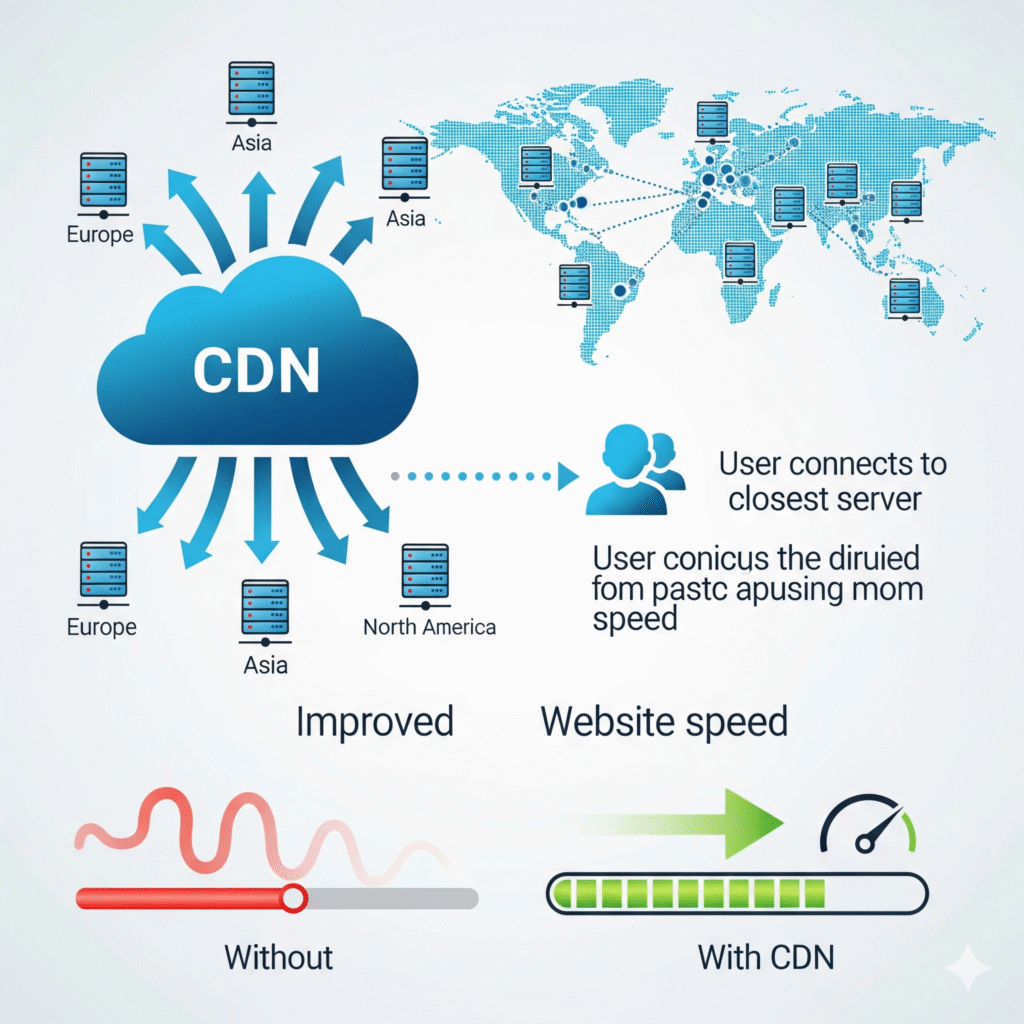
9) Add a CDN (Cloudflare works great)
Why: A CDN serves static assets from edge locations closer to your visitors, reducing latency and offloading your origin.
How:
- Create a free Cloudflare account and add your domain.
- Update nameservers as instructed.
- Enable Brotli, HTTP/2/3, Early Hints, and (if suitable) Auto Minify.
- Optionally, consider APO for WordPress (paid) for further edge caching—test with logins.
Important: Do not cache logged-in/admin pages or checkout.
10) Upgrade PHP & verify hosting foundations
Why: Newer PHP is faster and more memory-efficient; better hosting reduces I/O wait and spikes.
How (no code):
- In your hosting panel, switch to PHP 8.2/8.3. Test your site; roll back if a legacy plugin has issues.
- If TTFB is still slow even with caching, consider moving to LiteSpeed-based hosting (pairs well with LiteSpeed Cache).
Result: Lower server time across the board and better concurrency under traffic.

WooCommerce notes
- Don’t cache cart, checkout, or account pages (good plugins exclude them).
- Disable cart fragments on non-cart pages (e.g., Perfmatters toggle).
- Keep product pages light above the fold; move heavy widgets (reviews, related products) below.
- Optimize product images aggressively and preload the main product image.
Troubleshooting
- Menu/slider breaks after Delay JS: Add that script to the exclude list; clear cache.
- Brief unstyled flash (FOUC) after Unused CSS: Rebuild Critical CSS; ensure key theme CSS isn’t stripped.
- Blurry images after compression: Lower compression or raise resize cap to 1920px.
- 404s for fonts after localizing: Regenerate CSS/Critical CSS; confirm font files exist in uploads or the plugin folder.
FAQ
What’s the fastest way to improve WordPress performance?
Turn on page caching and compress/convert images to WebP—these usually deliver the biggest wins in minutes.
Can I speed up WordPress without coding?
Yes. With modern plugins, you can handle caching, lazy loading, JS/CSS optimization, fonts, and CDN entirely via toggles.
Do I need a new theme to get faster?
Not necessarily. However, moving from a heavy builder to a lightweight/block theme can unlock another jump.
Is Cloudflare required?
No. Even so, it’s a simple global speed boost on the free plan—especially for international audiences.
Will any of these tips break my site?
Rarely. Nevertheless, enable one feature at a time and retest critical pages after each change.
Final checklist
- Measure baseline (PSI + GTmetrix) for homepage and a key inner page
- Enable Page Cache; purge on publish
- Convert images to WebP/AVIF; cap width at 1600–1920px
- Turn on Lazy Load for images/iframes; exclude LCP image
- Defer and Delay non-critical JS; exclude any breaking files
- Remove Unused CSS or build Critical CSS
- Switch to system fonts or local Google Fonts + preload
- Disable heavy assets per page (Perfmatters/Asset CleanUp)
- Put site behind Cloudflare (Brotli + HTTP/2/3 + Early Hints)
- Upgrade to PHP 8.2/8.3; confirm plugin compatibility
- Schedule weekly DB cleanup
- Re-test and log improvements; update the post yearly
Wrap-up
Improving WordPress performance doesn’t require code—only a sequence. Start with caching and images, then layer in lazy loading, JS/CSS optimization, font fixes, CDN, and PHP upgrades. Because you measured before and after, you’ll see the exact gains in Core Web Vitals and, ultimately, in user engagement and revenue.
